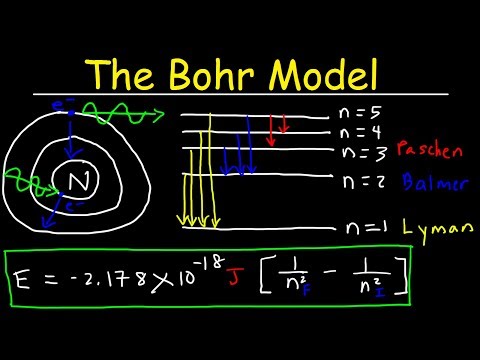
(ii) n = 4 to n = 3. As n increases, the energy levels gradually gets more closer. And, as a result hydrogen atom emits photon of lowest frequency in the transition.
Q. What is the value of ionisation energy for hydrogen atom?
13.6 eV
Table of Contents
- Q. What is the value of ionisation energy for hydrogen atom?
- Q. What is the value for hydrogen?
- Q. How would the ionization energy change when electron in hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle of mass 200 times that of the electron but having the same charge?
- Q. How would the ionization energy change when electron in hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle?
- Q. How does ionization change energy?
- Q. Does ionization increase from left to right?
- Q. Why does ionization energy increase and decrease?
- Q. Why the first ionization energy of oxygen is less than nitrogen?
- Q. Why is nitrogen ionization energy than oxygen?
Q. What is the value for hydrogen?
1.008
Q. How would the ionization energy change when electron in hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle of mass 200 times that of the electron but having the same charge?
Ionization energy is the minimum energy required to knock out an electron form an atom. When an electron in hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle 200 times heavier than electron, but having the same charge, ionization energy will not change, as it depends only on charge and not on mass of particle.
Q. How would the ionization energy change when electron in hydrogen atom is replaced by a particle?
Q. How does ionization change energy?
Moving left to right within a period or upward within a group, the first ionization energy generally increases. As the atomic radius decreases, it becomes harder to remove an electron that is closer to a more positively charged nucleus.
Q. Does ionization increase from left to right?
On the periodic table, first ionization energy generally increases as you move left to right across a period. This is due to increasing nuclear charge, which results in the outermost electron being more strongly bound to the nucleus.
Q. Why does ionization energy increase and decrease?
Ionization energy (IE) is the energy required to remove the highest-energy electron from a neutral atom. In general, ionization energy increases across a period and decreases down a group. The increased distance weakens the nuclear attraction to the outer-most electron, and is easier to remove (requires less energy).
Q. Why the first ionization energy of oxygen is less than nitrogen?
Oxygen also has an unexpectedly low ionisation energy, less than that of nitrogen. This is due to an electron being added to an already half full orbital in oxygen, which results in electron electron repulsion, which will lower the ionisation energy.
Q. Why is nitrogen ionization energy than oxygen?
Re: Why is ionization energy of oxygen lower than nitrogen? Nitrogen has a lower ionization energy than oxygen because nitrogen is half filled which according the Hund’s rule, half filled and full filled orbitals are more stable.