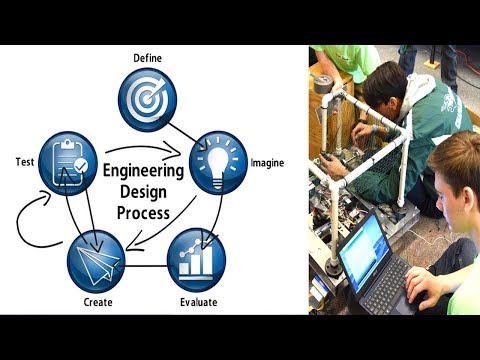
One example framing of the engineering design process delineates the following stages: research, conceptualization, feasibility assessment, establishing design requirements, preliminary design, detailed design, production planning and tool design, and production.
Q. What are the stages in design process?
Stages in the Design Process
Table of Contents
- Q. What are the stages in design process?
- Q. What is the third step in the engineering design process?
- Q. What is the purpose of design thinking?
- Q. What are the design thinking tools?
- Q. What is a design thinking approach?
- Q. What is mindset design thinking?
- Q. What are the 6 mindsets required for design thinking?
- Q. What is the most important skills of a design thinking leader?
- Q. What is a human-Centred approach?
- Q. What are the principles of human centered design?
- Q. What are the steps of human centered design thinking?
- Q. How do you use human centered design?
- Q. Why is human centered design important?
- Q. What is the difference between human centered design and design thinking?
- Analyze the situation. Before beginning the design, sort out what problem you are trying to address.
- Write a brief.
- Research the problem.
- Write a specification.
- Work out possible solutions.
- Select a preferred solution.
- Prepare working drawings and plan ahead.
- Construct a prototype.
Q. What is the third step in the engineering design process?
What Is the Engineering Design Process?
- Step 1: Define the Problem.
- Step 2: Do Background Research.
- Step 3: Specify Requirements.
- Step 4: Brainstorm, Evaluate and Choose Solution.
- Step 5: Develop and Prototype Solution.
- Step 6: Test Solution.
- Step 7: Does Your Solution Meet the Requirements?
- Step 8: Communicate Results.
Q. What is the purpose of design thinking?
Design thinking is a process for solving problems by prioritizing the consumer’s needs above all else. It relies on observing, with empathy, how people interact with their environments, and employs an iterative, hands-on approach to creating innovative solutions.
Q. What are the design thinking tools?
Best tools for each Design Thinking stage
- Empathize: Typeform, Zoom, Creatlr.
- Define: Smaply, Userforge, MakeMyPersona.
- Ideate: SessionLab, Stormboard, IdeaFlip.
- Prototype: Boords, Mockingbird, POP.
- Test: UserTesting, HotJar, PingPong.
- For the complete process: Sprintbase, InVision, Mural, Miro.
Q. What is a design thinking approach?
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation—anchored in understanding customer’s needs, rapid prototyping, and generating creative ideas—that will transform the way you develop products, services, processes, and organizations.
Q. What is mindset design thinking?
Design thinking is a deeply human process that taps into abilities we all have but get over-looked by more conventional problem-solving practices. Design thinking requires an experimental, collaborative, and optimistic mindset. We define mindset as the ideas and attitudes with which a person approaches a situation.
Q. What are the 6 mindsets required for design thinking?
To illustrate these themes further, we have broken them down into the following six key steps: frame a question, gather inspiration, generate ideas, make ideas tangible, test to learn, and share the story.
Q. What is the most important skills of a design thinking leader?
Answer. Answer: Design-thinking leaders know how to act as a catalyst for creativity.” Deeply understands the process of creative problem solving and knows how to act as a catalyst for creativity. Within the creative process, leaders should seek to be conduits, provocateurs, shepherds, and motivators.
Q. What is a human-Centred approach?
Human-centred design is an approach to interactive systems development that aims to make systems usable and useful by focusing on the users, their needs and requirements, and by applying human factors/ergonomics, and usability knowledge and techniques.
Q. What are the principles of human centered design?
The Four Principles of Human-Centered Design
- Understand and Address the Core Problems. Solve the fundamental, underlying issues, not the symptoms.
- Be People-Centered.
- Use an Activity-Centered Systems Approach.
- Use Rapid Iterations of Prototyping and Testing.
Q. What are the steps of human centered design thinking?
Design thinking is a popular methodology that inspires a human-centered approach to design. It is used by many design teams at some of the world’s most successful tech companies. The design thinking process is broken up into five specific design thinking stages: empathy, definition, ideation, prototyping, and testing.
Q. How do you use human centered design?
Here are the seven principles of Human-centred design.
- Get past your own great idea.
- Don’t be restricted by your own knowledge.
- Spend time with real people in real environments.
- Identify other users.
- Follow your users lead and needs.
- Think about the whole journey of the product.
- Prototype and test your idea.
Q. Why is human centered design important?
Human-centered design is a powerful way to understand evolving behaviors, preferences, and pain points and to focus efforts in the right places in the right ways. By unlocking the user’s perspective, designers can build solutions that work well and work widely in our new reality—whatever that ultimately looks like.
Q. What is the difference between human centered design and design thinking?
The most common explanation: Design thinking focuses on designing an object or process from scratch. Human Centered Design works to make an object or process that already exists (or is at least fully conceived) even better for users.